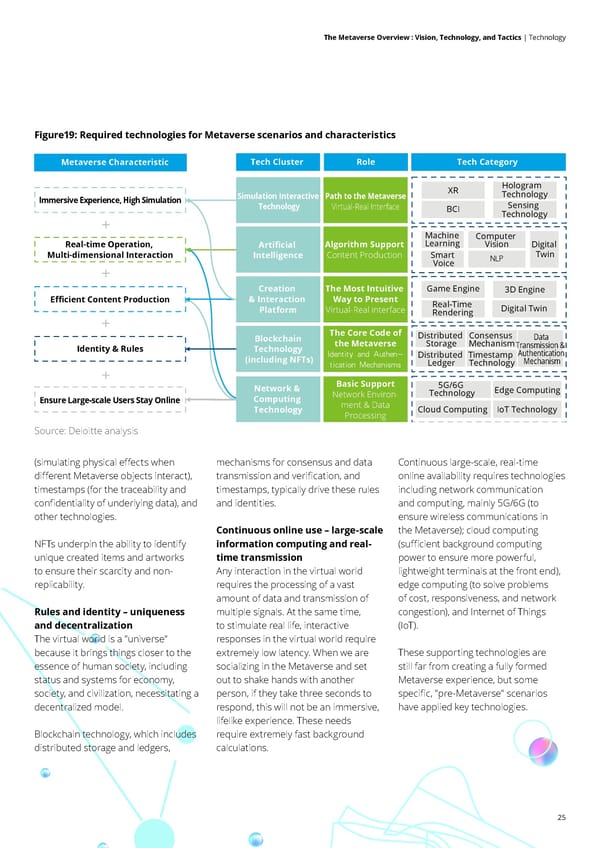
25 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Technology Ensure Large-scale Users Stay Online 5G/6G Technology Cloud Computing Edge Computing IoT Technology Immersive Experience, High Simulation XR BCI Hologram Technology Sensing Technology Real-time Operation, Multi-dimensional Interaction Machine Learning Smart Voice Computer Vision NLP Digital Twin Efficient Content Production Game Engine Real-Time Rendering 3D Engine Network & Computing Technology Simulation Interactive Technology Artificial Intelligence Creation & Interaction Platform Blockchain Technology (including NFTs) Identity & Rules Distributed Storage Distributed Ledger Consensus Mechanism Timestamp Technology Data Transmission & Authentication Mechanism Digital Twin Tech Cluster Role Tech Category Metaverse Characteristic Path to the Metaverse Virtual-Real Interface Algorithm Support Content Production The Most Intuitive Way to Present Virtual-Real interface The Core Code of the Metaverse Identity and Authen- tication Mechanisms Basic Support Network Environ- ment & Data Processing Figure19: Required technologies for Metaverse scenarios and characteristics Source: Deloitte analysis (simulating physical effects when different Metaverse objects interact), timestamps (for the traceability and confidentiality of underlying data), and other technologies. NFTs underpin the ability to identify unique created items and artworks to ensure their scarcity and non- replicability. Rules and identity – uniqueness and decentralization The virtual world is a "universe" because it brings things closer to the essence of human society, including status and systems for economy, society, and civilization, necessitating a decentralized model. Blockchain technology, which includes distributed storage and ledgers, mechanisms for consensus and data transmission and verification, and timestamps, typically drive these rules and identities. Continuous online use – large-scale information computing and real- time transmission Any interaction in the virtual world requires the processing of a vast amount of data and transmission of multiple signals. At the same time, to stimulate real life, interactive responses in the virtual world require extremely low latency. When we are socializing in the Metaverse and set out to shake hands with another person, if they take three seconds to respond, this will not be an immersive, lifelike experience. These needs require extremely fast background calculations. Continuous large-scale, real-time online availability requires technologies including network communication and computing, mainly 5G/6G (to ensure wireless communications in the Metaverse); cloud computing (sufficient background computing power to ensure more powerful, lightweight terminals at the front end), edge computing (to solve problems of cost, responsiveness, and network congestion), and Internet of Things (IoT). These supporting technologies are still far from creating a fully formed Metaverse experience, but some specific, "pre-Metaverse" scenarios have applied key technologies.
 Deloitte The Metaverse Overview Page 24 Page 26
Deloitte The Metaverse Overview Page 24 Page 26