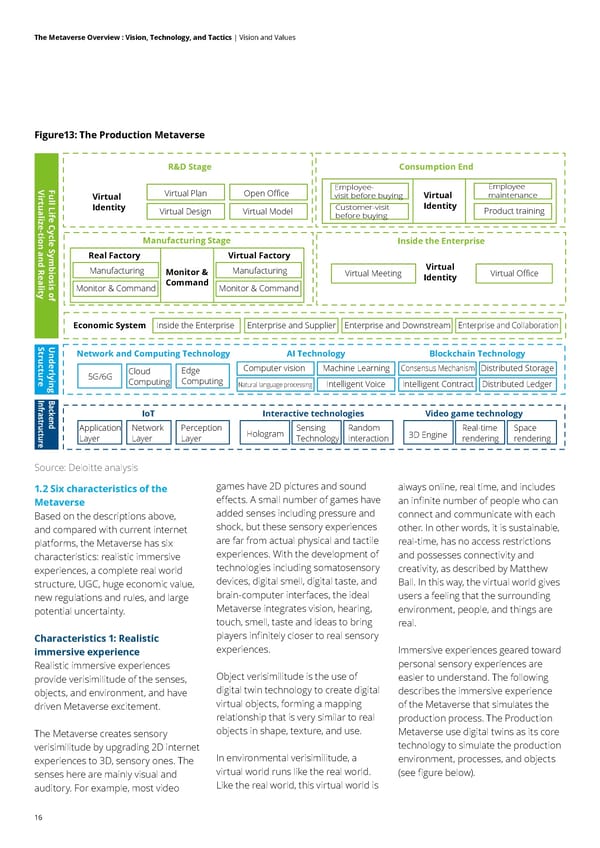
16 The Metaverse Overview : Vision, Technology, and Tactics | Vision and Values Figure13: The Production Metaverse Source: Deloitte analysis 1.2 Six characteristics of the Metaverse Based on the descriptions above, and compared with current internet platforms, the Metaverse has six characteristics: realistic immersive experiences, a complete real world structure, UGC, huge economic value, new regulations and rules, and large potential uncertainty. Characteristics 1: Realistic immersive experience Realistic immersive experiences provide verisimilitude of the senses, objects, and environment, and have driven Metaverse excitement. The Metaverse creates sensory verisimilitude by upgrading 2D internet experiences to 3D, sensory ones. The senses here are mainly visual and auditory. For example, most video games have 2D pictures and sound effects. A small number of games have added senses including pressure and shock, but these sensory experiences are far from actual physical and tactile experiences. With the development of technologies including somatosensory devices, digital smell, digital taste, and brain-computer interfaces, the ideal Metaverse integrates vision, hearing, touch, smell, taste and ideas to bring players infinitely closer to real sensory experiences. Object verisimilitude is the use of digital twin technology to create digital virtual objects, forming a mapping relationship that is very similar to real objects in shape, texture, and use. In environmental verisimilitude, a virtual world runs like the real world. Like the real world, this virtual world is always online, real time, and includes an infinite number of people who can connect and communicate with each other. In other words, it is sustainable, real-time, has no access restrictions and possesses connectivity and creativity, as described by Matthew Ball. In this way, the virtual world gives users a feeling that the surrounding environment, people, and things are real. Immersive experiences geared toward personal sensory experiences are easier to understand. The following describes the immersive experience of the Metaverse that simulates the production process. The Production Metaverse use digital twins as its core technology to simulate the production environment, processes, and objects (see figure below). R&D Stage Network and Computing Technology 5G/6G Cloud Computing Edge Computing AI Technology Computer vision Machine Learning Natural language processing Intelligent Voice Blockchain Technology Consensus Mechanism Distributed Storage Intelligent Contract Distributed Ledger IoT Application Layer Network Layer Perception Layer Interactive technologies Hologram Sensing Technology Random Interaction Video game technology 3D Engine Real-time rendering Space rendering Consumption End Manufacturing Stage Inside the Enterprise Economic System Inside the Enterprise Enterprise and Supplier Enterprise and Downstream Enterprise and Collaboration Virtual Plan Virtual Identity Full Life Cycle Symbiosis of Virtualize-tion and Reality Underlying Structure Backend Infrastructure Virtual Design Virtual Model Open Office Virtual Identity Employee- visit before buying Employee maintenance Monitor & Command Real Factory Virtual Factory Manufacturing Monitor & Command Customer-visit before buying Product training Virtual Meeting Virtual Identity Virtual Office Manufacturing Monitor & Command
 Deloitte The Metaverse Overview Page 15 Page 17
Deloitte The Metaverse Overview Page 15 Page 17